Ever wonder how complex applications, like a sprawling e-commerce site, manage to keep all their moving parts in sync without falling apart? The secret often lies in a powerful tool like Azure Service Bus.
At its heart, Azure Service Bus is a fully managed enterprise message broker. But what does that really mean?
Think of it as a sophisticated digital post office for your applications. It provides a central, reliable place for different parts of your system to drop off and pick up messages. This simple concept is what allows modern applications to be both resilient and scalable, ensuring messages get delivered even if the intended recipient is temporarily busy or offline.
What Is Azure Service Bus in Simple Terms?
Let's stick with that e-commerce platform example. It isn't just one giant program. It's actually a collection of smaller, independent services working together. You'll have a service for user accounts, another for processing orders, one for inventory, and yet another for sending shipping notifications.
In a less robust system, these services might call each other directly. When an order is placed, the order service has to directly tell the inventory service, then the shipping service, and finally the notification service. This "tightly coupled" design is incredibly fragile.
The Problem with Direct Communication
What happens if the inventory service goes down for a quick update right as a new order comes in? The whole process grinds to a halt. Or imagine a Black Friday sale. The sudden flood of orders could easily overwhelm the notification service, causing it to crash and lose track of which customers need updates.
This is precisely the problem Azure Service Bus was built to solve. It steps in as the middleman. Now, the order service can just drop off an "Order Placed" message in a central location and move on, completely unaware of whether the other services are ready to handle it.
To give you a quick overview, here's a summary of what Azure Service Bus brings to the table.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Fully managed enterprise message broker |
| Core Function | Decouples applications by enabling asynchronous communication |
| Key Components | Queues (one-to-one), Topics & Subscriptions (one-to-many) |
| Main Benefit | Improves application reliability, scalability, and flexibility |
This intermediary model is what makes modern, distributed systems work so effectively.
Key Takeaway: The primary role of Azure Service Bus is to decouple applications. By allowing services to communicate asynchronously—meaning they don't have to be active at the same time—it dramatically boosts the reliability and scalability of your entire system.
This approach immediately unlocks several critical advantages:
- Load Balancing: If a service gets slammed with requests, the messages simply wait patiently in a queue. This prevents services from crashing during traffic spikes.
- Enhanced Reliability: Messages are held securely in the Service Bus until the receiving application confirms it has successfully processed them. If a receiver crashes mid-task, the message isn't lost and can be retried.
- Greater Flexibility: You can update, replace, or add new services without disrupting the flow. The inventory service can be taken offline for maintenance; when it comes back, it will just start processing the orders that have queued up.
This messaging pattern is a cornerstone of modern cloud architecture. The growing demand for these robust communication tools is clear. The enterprise service bus (ESB) software market, which includes platforms like Azure Service Bus, was valued at $1.12 billion and is projected to hit $2.07 billion by 2033. You can learn more about these market trends and see why this technology is so fundamental to building resilient applications.
Understanding the Building Blocks of Service Bus
To really get a handle on what Azure Service Bus can do, you need to know its core components. These are the fundamental pieces you'll use to build tough, scalable messaging systems. Let's break down the three essentials: Namespaces, Queues, and Topics.
I find it helpful to think of these parts like a digital postal system. Each one has a specific job, but they all work together to make sure your messages get where they need to go, right on time.
The Foundation: Your Namespace
Everything starts with the Namespace. You can picture the Namespace as the entire post office building. It's a dedicated, unique container in Azure that holds all your messaging components—your Queues and your Topics.
When you spin up a new Service Bus instance, the first thing you're actually creating is this Namespace. It gives you a unique domain name (an FQDN) that your applications use to connect. Essentially, it's the address for your entire messaging operation, keeping your app's messages neatly separated from everyone else's on Azure. Every single Queue or Topic you make will live inside this container.
Queues: The Direct Delivery Route
Once you have your Namespace, one of the most common things you'll create is a Queue. Sticking with our postal analogy, a Queue is like a private mailbox for a single recipient. It’s built for simple, one-to-one communication between two different parts of your application.
Here's how it works: a sender application drops a message into the Queue, and a single receiver application picks it up to process it. This creates what we call temporal decoupling, which is just a fancy way of saying the sender and receiver don't have to be online at the same time. The message just waits safely in the Queue until the receiver is ready for it.
This setup is perfect for jobs like:
- Order Processing: An e-commerce site can send an "order created" message to a Queue. A separate order processing service can then grab that message whenever it has the bandwidth.
- Task Offloading: A web app can offload a heavy task, like generating a big report, by sending a request to a Queue. A background worker can then pick it up and do the heavy lifting without slowing down the user-facing app.
A fantastic feature of Queues is the competing consumer pattern. If you have several receivers listening to the same Queue, only one of them will successfully grab and process any given message. This makes it incredibly easy to scale out your processing power—just add more receivers.
This diagram shows how everything fits together in Azure Service Bus, highlighting how core features like messaging, security, and reliability are all interconnected.
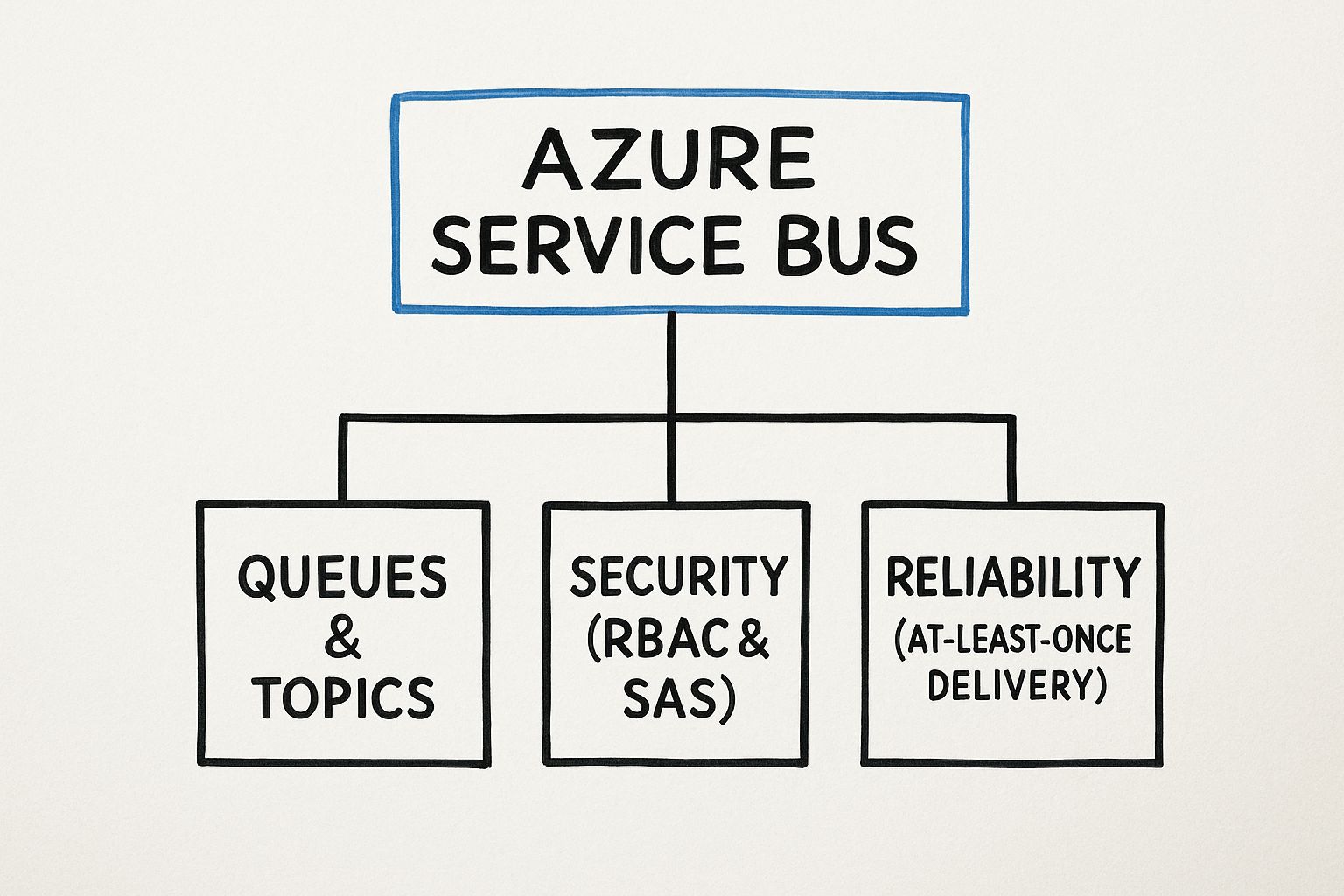
The image makes it clear: while Queues and Topics are the workhorses for messaging, they're built on a solid foundation of security and reliability that makes the whole service so powerful.
Topics: The Broadcast System
Queues are great for one-to-one messaging, but what if you need to shout an announcement for anyone who's interested? That's exactly what Topics are for. A Topic is like a public bulletin board or a news feed. A publisher sends one message to the Topic, and many different systems can each get their own copy.
So, how do they get their copy? Through Subscriptions. A Subscription is basically a virtual queue that's tied to a specific Topic. Each Subscription gets a fresh copy of every single message that's sent to the Topic it's listening to.
Let's go back to our e-commerce store example:
- A single "Order Placed" event is published to an
OrderTopic. - Several services are interested in this event, and each has its own Subscription to the
OrderTopic:- The
InventoryServicesubscribes so it can update stock levels. - The
ShippingServicesubscribes to start preparing the package for shipment. - The
AnalyticsServicesubscribes to track sales trends in real-time.
- The
Each service gets its own independent copy of the message from its own subscription. They can all work in parallel without ever stepping on each other's toes. This is the classic publish/subscribe (or pub/sub) pattern, and it’s the bedrock of modern, flexible, event-driven systems. You can add new subscribers or remove old ones whenever you want, without ever touching the original publishing application. Frankly, this incredible flexibility is one of the biggest reasons developers turn to Azure Service Bus.
How Service Bus Manages Your Messages
Now that we've covered the basic building blocks of Queues and Topics, we can dig into how Azure Service Bus actually orchestrates the flow of communication. It’s about more than just getting a message from point A to point B; it’s about managing that message's entire journey with real precision and rock-solid reliability. This is where you start to see the service's true power and how it solves complex, real-world development headaches.
The two main patterns you'll work with are direct communication and the publish/subscribe model. Think of a Queue as a direct, one-to-one line, making sure a message is handled by only one receiver. In contrast, a Topic acts like a broadcast system, fanning out a single message to many different subscribers who might be interested. Getting this distinction right is fundamental to building a robust architecture. The market seems to agree on its effectiveness; within the messaging software space, Azure Service Bus holds a 3.40% market share, serving over 1,602 customers. You can see how it stacks up against the competition if you're curious.
While these patterns are the foundation, the advanced features provide the fine-tuned control you need for serious, enterprise-level applications. Let's walk through some of these features using a practical e-commerce example.
Ensuring Order with Message Sessions
Picture this: a customer updates their shipping address a few times right before their order is processed. If those "address update" messages arrive out of order, you could easily ship their package to the wrong place. That’s a real problem, and it's exactly what Message Sessions are designed to prevent.
Message Sessions essentially create a dedicated, private lane for a group of related messages. By tagging all messages for a specific order with the same session ID (like order-123), you guarantee they are handled in sequence by a single receiver. This first-in, first-out (FIFO) behavior within a session is absolutely critical for any process that demands strict ordering.
- Create Order: The session
order-123is started. - Update Address: This message gets locked to the
order-123session. - Process Payment: This one is also locked to the
order-123session.
A receiver then locks the entire session, processes all of its messages in the correct sequence, and only then releases the lock. This simple mechanism prevents another part of your system from accidentally grabbing a later message and processing it out of turn.
Handling Problems with Dead-Lettering
So, what happens when a message just can't be processed? Maybe an order contains a product ID that doesn't exist, or the payment gateway is down for a moment. Instead of letting that broken message jam up the main queue or get stuck in a frustrating retry loop, Service Bus gives you a safety net: the dead-letter queue (DLQ).
Every Queue or Subscription automatically gets its own secondary DLQ. When a message fails to process after a few tries or breaks a rule (like its time-to-live expiring), Service Bus automatically shunts it over to the DLQ.
Key Insight: The dead-letter queue isn't a digital graveyard. It’s more like an isolation ward for problematic messages. It lets you inspect, fix, and even resubmit them later, all without bringing your main application to a halt. This is a must-have for building resilient systems that can handle the unexpected.
In our e-commerce example, an order with a bad customer ID would land in the DLQ. The main system keeps chugging along, processing valid orders without interruption, while a developer or an automated tool can investigate the dead-lettered message to figure out what went wrong.
Scheduling with Message Deferral and Timestamps
Not every task needs to happen right away. Sometimes you need to schedule something for the future or just delay it for a bit. Service Bus has two great features for this.
- Scheduled Messages: You can set a property on a message called
ScheduledEnqueueTimeUtc, telling Service Bus to keep it on ice until that exact moment. This is perfect for things like sending a "Your order has shipped!" email exactly 24 hours after you confirm shipment. - Message Deferral: This one is a bit different. A receiver can peek at a message but decide it's not ready to handle it yet. Instead of just letting it go, the receiver can "defer" it by taking note of its unique sequence number. The message stays in the queue but is hidden from other receivers until it's specifically requested again using that sequence number. This comes in handy for complex workflows where one step depends on another that isn't quite finished.
Putting Azure Service Bus into Practice
Alright, we've covered the components and patterns. But theory only gets you so far. The real magic happens when you see how Azure Service Bus solves actual business problems, making systems more resilient, scalable, and a whole lot easier to manage.
At its heart, Service Bus is all about decoupling. It lets different parts of an application talk to each other without being directly wired together. This simple concept is a game-changer, allowing your systems to handle failures gracefully and grow without needing a complete architectural tear-down.
Orchestrating Complex E-Commerce Operations
Think about an e-commerce platform. When a customer places an order, it kicks off a whole chain of events. Service Bus acts as the central traffic cop, making sure every step happens reliably—especially during a chaotic event like a Black Friday sale.
Imagine an OrderPlaced Topic managing the entire process:
- Payment Processing: The order system publishes a message to the
OrderPlacedtopic. The payment service, a subscriber, picks it up, processes the payment, and then publishes its own message to aPaymentConfirmedtopic. - Inventory Management: The inventory system, listening to the
PaymentConfirmedtopic, gets the message and immediately deducts the item from stock. This simple step is crucial for preventing overselling. - Shipping and Logistics: Meanwhile, the shipping department’s system, also subscribed to
PaymentConfirmed, gets the green light to start fulfillment—from picking the item to printing the shipping label. - Customer Notifications: A separate notification service listens in, grabs the details, and sends the customer an order confirmation email.
If you tried to build this without a message broker, the whole process would be brittle. If the email service went down, the entire order might fail. With Service Bus, the "send notification" message just sits patiently in its subscription queue until the service is back online. That’s the difference between a fragile system and a truly robust one.
The real power here is adaptability. What if you want to add a new fraud detection service? Simple. You just create a new subscription to the
OrderPlacedtopic. The original order-taking application doesn't need a single line of code changed. That's incredible flexibility.
Ensuring Reliability in Financial Services
The financial world runs on precision and trust. Transactions have to be processed correctly, in the right order, and without a single byte of data getting lost. This is where the more advanced features of what is Azure Service Bus really prove their worth.
Take a stock trading platform. A flurry of trades from a single user must be executed exactly as they were placed. By using Message Sessions, the platform can group all trades from one user together. This guarantees a "buy" order is always handled before that same user's "sell" order for the same stock, preventing costly sequencing mistakes.
For critical operations like fund transfers, guaranteed delivery is non-negotiable. Service Bus ensures that once a "transfer funds" message is accepted, it will be processed at least once, even if parts of the system crash and need to restart.
Connecting Disparate Systems in Healthcare
Healthcare is notorious for having specialized systems that just don't play well together. You’ve got one system for patient records (EHR), another for lab results, and a third for billing. Service Bus can step in as the universal translator and delivery service.
When a doctor orders a lab test, the EHR system can publish a message to a LabTestOrdered topic. The lab's system (LIS) subscribes, picks up the order, and runs the test. Once the results are in, the LIS publishes a ResultsReady message, which the EHR system consumes to update the patient's file. This asynchronous flow means each system can be updated or maintained on its own schedule without disrupting patient care.
The adoption of Azure Service Bus is surprisingly broad. Recent data shows it’s not just for big players; 39% of its customers are small businesses, while 37% are large corporations. The top industries using it are Information Technology (31%), Computer Software (14%), and Financial Services (6%), showing just how versatile it is. You can discover more about Azure Service Bus customer demographics to get a bigger picture.
These examples aren't just hypotheticals. They show that Service Bus is a practical, powerful tool for building modern applications you can actually depend on.
Choosing the Right Service Bus Pricing Tier
Picking the right pricing tier in Azure Service Bus is a decision that has a real impact on your application's performance, what it can do, and how much you'll spend. Microsoft offers three tiers—Basic, Standard, and Premium—and each is built for a different kind of job. If you get this choice wrong, you could end up paying for power you don't need or, worse, starving a critical system that needs more muscle.
I like to think of it like picking an internet plan for your house. You wouldn't spring for a gigabit fiber connection just to check email, and you certainly wouldn't try streaming 4K movies over an old dial-up line. It's the same idea here. The goal is to match the tier's capabilities with your application's real-world needs for scale, reliability, and budget.
A Breakdown of the Three Tiers
Each tier is a step up from the one before it, adding more features and boosting performance. Let's dig into what each one is really for, so you can choose wisely.
-
Basic Tier: This is your starting line. The Basic tier is really just for development, testing, and other non-critical tasks. It only gives you Queues and comes with some pretty strict limits on things like message size and storage. It’s perfect for getting your feet wet and learning the ropes without a big investment, but it’s not built for the demands of a live production environment.
-
Standard Tier: For most production applications, this is the sweet spot. The Standard tier is the workhorse of the family, bringing Topics and Subscriptions into the mix. This unlocks the incredibly useful publish/subscribe pattern, which is a game-changer for many architectures. It also adds crucial features like duplicate detection and transactions, giving you the reliability you need to run a real business.
-
Premium Tier: When you absolutely cannot compromise on performance and predictability, you need the Premium tier. This tier gives you dedicated, isolated resources, meaning your workload won't be slowed down by other customers on the platform. The result is consistently low latency and high throughput, which is non-negotiable for enterprise-grade, mission-critical systems.
The performance jump to Premium is no joke. According to Microsoft's own benchmarks, some workloads have seen performance gains of over 150% since the tier was first introduced. For anyone studying for the AZ-204 exam, knowing these differences is vital, as it's a common topic. If you're in that boat, check out resources like AZ-204 Fast for some targeted practice.
My Two Cents: Stick with the Standard tier for most production apps that need a good balance of features and cost. Only move to Premium when you need guaranteed performance, dedicated hardware, and advanced features like geo-disaster recovery for your most important workloads.
Azure Service Bus Tiers Comparison
To lay it all out, a side-by-side comparison can make the choice much clearer. This table shows you exactly what you get as you move up the ladder from Basic to Premium.
| Feature | Basic Tier | Standard Tier | Premium Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | Development & Testing | General Production | Mission-Critical Systems |
| Topics & Subscriptions | No | Yes | Yes |
| Resource Model | Shared | Shared | Dedicated |
| Performance | Variable | Good | Predictable & High |
| Geo-Disaster Recovery | No | No | Yes |
| VNet Integration | No | No | Yes |
As you can see, the decision really boils down to a trade-off between cost and capability.
Ultimately, start by mapping out what your application truly requires. Do you need to send a single message to multiple downstream systems? Then you need Standard or Premium for Topics. Is predictable, lightning-fast performance essential for processing financial transactions? Premium is your only real option. By answering these kinds of practical questions, you can confidently pick the tier that gives you the right power at the right price.
Why Adopting Service Bus Is a Smart Move
Bringing a tool like Azure Service Bus into your application architecture is more than just a technical tweak—it's a strategic move. It fundamentally changes how your services talk to each other, creating a system that's far more reliable, scalable, and ready for whatever comes next. The real magic lies in its ability to decouple your application's components.
This separation immediately makes your entire system more resilient. Service Bus offers durable messaging, which is a fancy way of saying it holds onto messages securely until the receiving application is ready for them. So, if a downstream service crashes or needs to be taken offline for an update, no data is lost. Messages just wait patiently in a queue, preventing the kind of data loss that can be disastrous in tightly connected systems.
Scale Services Independently
One of the biggest wins you get is the power to scale different parts of your system independently. In a classic, monolithic setup, a traffic spike in one corner can ripple through and take down everything. With Service Bus acting as the middleman, each service can scale on its own based on the message load it's facing.
Think about an e-commerce site running a flash sale. The order processing service might get hammered, but that won't stop the website from accepting new orders. Those orders simply line up in a queue, and you can automatically spin up more instances of the processing service to work through the backlog. This elastic scaling keeps the user experience smooth even under intense pressure, which directly protects your revenue and reputation.
This kind of robust traffic management is a big reason why Microsoft was named a Leader in the 2024 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Integration Platform as a Service for the sixth consecutive time. You can learn more about this recognition of Microsoft's integration capabilities on their official blog.
Achieve Greater Development Agility
Decoupling also unlocks a ton of development flexibility. When services aren't tied directly to each other's code, your teams can work on them in parallel, which really speeds up development. You can update, replace, or even completely rebuild a single service without having to coordinate a massive, all-hands-on-deck deployment.
For instance, you could decide to swap out an old email notification service for a shiny new one that also sends push notifications. The new service just needs to start listening to the same message topic, and the switch happens without the core order system ever knowing anything changed.
The Bottom Line: Adopting Azure Service Bus reduces operational risk while boosting your ability to adapt. It helps you build systems that not only handle today's workload but are also ready to grow and evolve with your business, letting you innovate faster and with more confidence.
This agility is why so many developers focus on mastering these concepts for their certifications. If you're studying for the AZ-204 exam, a deep understanding of Service Bus is non-negotiable. Tools like AZ-204 Fast are designed specifically to help you get a firm grip on these critical architectural patterns so you can walk into your exam with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions About Azure Service Bus
Now that we've covered the fundamentals of Azure Service Bus, let's tackle some of the common questions that pop up when you start putting these concepts into practice. Think of this as the practical "how-to" part of the conversation, designed to clear up any lingering confusion and help you make smarter architectural choices.
Azure Service Bus vs. Event Grid
One of the most common head-scratchers for developers new to Azure messaging is figuring out the difference between Azure Service Bus and Azure Event Grid. They both deal with messages, but they're built for entirely different jobs.
Here’s a simple analogy: think of Service Bus as a registered mail service for delivering critical business packages. It ensures the package gets there, in order, and is signed for. Event Grid, on the other hand, is like a news alert system—it broadcasts lightweight notifications that something happened.
-
Azure Service Bus is all about transactional messaging. It’s for sending commands or business data that must be processed, like "place this order" or "update this customer record." It uses a pull model, where a receiver actively fetches messages from a queue when it's ready.
-
Azure Event Grid is built for event-driven architecture. It reacts to state changes—things that have already happened, like "a new blob was created in storage" or "a virtual machine has started." It uses a push model, automatically sending notifications out to anyone who has subscribed to that event.
The Bottom Line: Reach for Service Bus when you need iron-clad reliability, message ordering, and complex processing for critical operations. Go with Event Grid when you need to simply react to events happening across your Azure ecosystem with a lightweight, push-based system.
When to Use a Queue Instead of a Topic
Choosing between a Queue and a Topic really comes down to one simple question: how many different systems need to hear about this message?
You should use a Queue for straightforward, one-to-one communication. When a message is sent to a queue, it's destined for a single receiver to pick it up and process it. This is perfect for offloading a specific task to a background worker, ensuring only one worker grabs the job. A great example is a request to generate a PDF report—you only want one service to do that work.
Use a Topic for one-to-many communication, often called the publish/subscribe (or "pub/sub") pattern. Here, a publisher sends just one message to the topic, and multiple, independent subscribers can each get their own copy to act on. This is ideal when a single event needs to kick off several different processes. For instance, a new customer order might need to trigger an inventory update, a confirmation email, and a notification to the shipping department all at once.
Can Azure Service Bus Be Used for Real-Time Communication?
In a word, no. Azure Service Bus is not the right tool for real-time applications like a live chat or a multiplayer game. Its purpose is to enable asynchronous messaging.
What does that mean? It’s designed to decouple your applications, so the sender and receiver don't need to be online and available at the exact same moment. It prioritizes reliability and guaranteed delivery over instantaneous communication.
While messages in Service Bus are often delivered with very low latency, its core strengths are managing queues and ensuring a message will get there eventually. For true, real-time, two-way communication between a server and its clients, you'd want to use a dedicated service like Azure SignalR Service. Service Bus makes sure your message arrives reliably; SignalR makes sure it arrives right now.
Passing your certification exam requires more than just reading—it demands active recall and targeted practice. AZ-204 Fast provides the focused tools you need, with interactive flashcards and dynamic practice exams designed to build deep knowledge and confidence. Conquer the AZ-204 exam efficiently with our evidence-based learning platform at https://az204fast.com.
Leave a Reply