That sinking feeling you get staring at a spreadsheet that needs hours of manual data entry? We've all been there. But what if you could knock out that tedious work in a few seconds? That's exactly what Excel's Autofill feature is for, and it’s a non-negotiable skill for anyone who wants to get serious with spreadsheets.
Why Autofill Is Your Most Powerful Ally in Excel
Think of Autofill as more than just a handy shortcut—it’s the engine that drives efficient data management in Excel. It takes the soul-crushing task of repetitive data entry and turns it into a swift, automated process. This is where you start to see the hidden power of a feature you thought you already knew. Whether you're a seasoned financial analyst or just starting out, mastering it is the key to unlocking a whole new level of productivity.
The real magic of Autofill is its ability to recognize patterns. It doesn't just copy and paste; it intelligently predicts what you're trying to do, saving you an incredible amount of time and effort. This intuitive power is a huge reason why Excel became the global standard it is today. With an estimated 1.1 to 1.5 billion users worldwide, it's core features like Autofill that make it indispensable. You can dig deeper into Excel's global impact on scottmax.com.
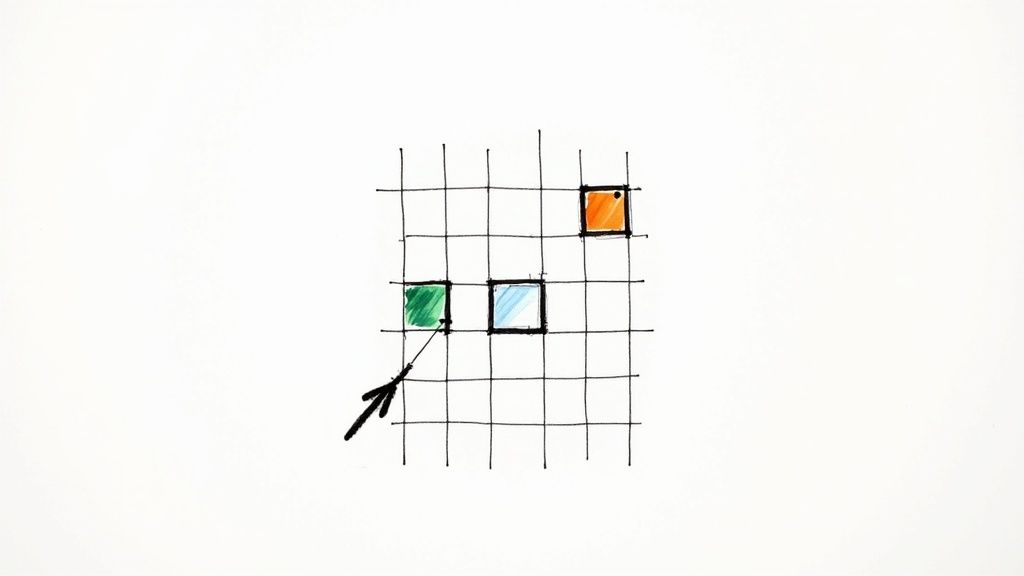
What Makes Autofill Essential
Getting a grip on Autofill lets you move past basic spreadsheet tasks and start handling data with genuine speed and accuracy. The payoff is immediate: less time spent on grunt work and fewer errors in your data.
Here’s what you gain:
- Drastic Time Reduction: Forget typing things out one by one. Instantly populate hundreds or even thousands of cells with sequential data, whether it’s dates, numbers, or custom lists.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Automation is your best defense against typos. By letting Excel create the series for you, you eliminate the risk of manual errors that can throw off an entire dataset.
- Enhanced Workflow Efficiency: It makes common tasks almost effortless. Think about creating project timelines, numbering inventory lists, or setting up monthly financial reports—Autofill handles it all.
The goal isn't just to learn how to drag a handle; it's to build your confidence by solving common spreadsheet challenges with speed and precision, making these functions second nature.
At the end of the day, knowing how to use autofill in excel effectively is what separates a casual user from a true power user. It lets the software do the heavy lifting, freeing you up to focus on the important stuff—like analysis and strategy—instead of getting bogged down in mind-numbing data entry.
Everyday Tasks Made Easy with the Fill Handle
The quickest way to get started with Autofill in Excel is by using the fill handle. It’s that small, solid square you see in the bottom-right corner of any cell you select. When you hover your mouse over it, the cursor changes into a thin black cross. That’s your cue to click and drag.
Let's try a common scenario: building a weekly project schedule. You type "Monday" into cell A1. Instead of typing out the rest of the week by hand, just click on cell A1, grab that little fill handle, and drag it down. Like magic, Excel fills in "Tuesday," "Wednesday," and so on.
The same logic works for numbers, dates, and even custom patterns. Need to create an inventory list with 100 numbered items? Don't type 1, 2, 3… all the way down the column. Just enter "1" in the first cell and "2" in the cell right below it. Then, select both cells to show Excel the pattern you want, grab the fill handle, and pull it down. Excel gets the hint and continues the sequence for you.
Getting More Control with Autofill Options
Right after you drag the fill handle and let go of the mouse, a small icon pops up. This is the Autofill Options menu, and it’s where you can fine-tune what Excel just did. Clicking it reveals a menu that gives you much more precise control.
For instance, if you drag a date down a column, this menu lets you choose exactly how you want the series filled:
- Fill Days: This is the default. It simply adds one day at a time.
- Fill Weekdays: Incredibly useful for business schedules, this option automatically skips Saturdays and Sundays.
- Fill Months: If your first cell was "January," this will fill in "February," "March," and so on.
- Fill Years: This bumps the year up by one while keeping the month and day the same.
The image below gives you a perfect visual of this in action. Dragging the fill handle from a cell with "Jan" instantly creates the next few months.
It’s a simple drag-and-drop that creates a logical series, saving you a ton of time and effort.
Practical Scenarios You'll Use Constantly
Knowing the tool is one thing, but actually using it is what makes you an expert. Think about when you're creating a monthly sales report. You can pop "Jan-24" into a cell, drag the fill handle, and create a timeline for the entire year in less than three seconds. No more pulling up a calendar or typing each month manually.
The real power of the fill handle isn't just about saving a few keystrokes. It's about removing the mental drag of repetitive work, which frees you up to focus on what the data actually means.
This simple tool is also a lifesaver in finance for projecting quarterly results. If you establish a pattern like "Q1," "Q2," Excel will happily complete the rest for you. Honing these small but mighty skills is a huge part of becoming more efficient with data. In fact, if you're building up your tech skills, you might find our guide on how to get Microsoft certified useful, as mastering tools like this is a stepping stone to more advanced data management.
Exploring Advanced Autofill Techniques
Once you get the hang of dragging the fill handle, you're ready to see what Excel's Autofill can really do. This is where you graduate from filling simple sequences to automating custom data entry, saving yourself a massive amount of time. Let's start with a real game-changer: creating your own Autofill series.
Think about the unique lists you use all the time at work. Maybe it’s a specific set of project codes, a list of department names, or your company's regional offices. Instead of hunting down that list and copy-pasting it every single time, you can actually teach Excel to remember it.
By creating a custom list, you're basically adding your unique series to Excel's brain. Once it's set up, you can just type the first item in your list—say, "North Region"—grab the fill handle, and watch Excel instantly populate "East Region," "South Region," and "West Region" in perfect order. It’s incredibly efficient.
Build Your Own Custom Lists
Setting up a custom list is surprisingly straightforward and the payoff is immediate. You can find this feature tucked away in Excel's settings, usually under the "Advanced" tab. Once you create a list, it’s there for good, ready to use in any workbook. This gives you total control over the text-based series you rely on most.
Autofill with Formulas and References
This is where Autofill becomes a true powerhouse. When you drag the fill handle on a cell that contains a formula, Excel is smart enough to adjust the cell references for each new row or column. This is called a relative reference. For instance, if your formula in C1 is =A1+B1 and you drag it down, it automatically becomes =A2+B2 in cell C2, then =A3+B3, and so on.
But what if you need part of your formula to stay locked on a single cell? Imagine you have a fixed budget amount in cell E1 that needs to be part of the calculation for an entire column of expenses. That’s where absolute references come in. By adding a dollar sign ($) before the column letter and row number (like this: =$E$1), you’re telling Excel, "Hey, don't change this part when you autofill."
Pro Tip: Honestly, getting comfortable with the difference between relative (
A1) and absolute ($A$1) references is one of the most critical skills you can learn in Excel. It's the foundation for building dynamic, scalable spreadsheets that don't break.
This technique is fundamental to business budgeting. Even with all the new software out there, Excel's powerful features like this are why it remains so dominant. While overall Excel usage for budgeting in the US dipped from 79% in 2017 to 54% in 2019, a solid 59% of small businesses still named it their main budgeting tool. You can dig into the numbers in this report on Excel's business dominance.
Meet Flash Fill: Your Smart Assistant
Beyond the standard Autofill, Excel has an even smarter cousin called Flash Fill. This tool is almost magical. It detects patterns in your data and fills in the rest for you without you even having to write a formula.
For example, say you have a column of full names ("John Smith," "Jane Doe," etc.) and you start typing just the first names ("John") in the column next to it. Flash Fill will instantly recognize what you're doing and offer to extract all the first names for you. Just hit Enter, and the job is done. It’s perfect for cleaning up messy data—like splitting full addresses into street, city, and state, or reformatting phone numbers on the fly.
Autofill vs Flash Fill Key Differences
While they might seem similar, Autofill and Flash Fill are designed for very different jobs. Knowing when to use each one will make your workflow much smoother. Here’s a quick breakdown.
| Feature | Autofill | Flash Fill |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Extending a predictable series (numbers, dates, custom lists, formulas). | Extracting, combining, or reformatting data based on a pattern you show it. |
| How it Works | You provide the starting point(s), and it follows a logical or predefined sequence. | It analyzes an example you provide and applies that pattern to the rest of the column. |
| Data Type | Works great with numbers, dates, times, and any text in a custom list. | Excels at manipulating text and numbers already present in adjacent cells. |
| Example | Typing "Jan" and dragging down to get "Feb," "Mar," etc. | Typing "Smith" next to "John Smith" to extract all last names. |
In short, use Autofill when you need to continue a sequence. Use Flash Fill when you need to transform existing data.
Time-Saving Autofill Shortcuts and Pro Tips
Knowing the basics of autofill in Excel is one thing, but the real magic happens when you master the shortcuts. These are the little tricks that experienced users rely on to fly through their work, turning tedious data entry into a task that takes just a few seconds.
Let’s start with my absolute favorite: the double-click method. Picture this: you have a massive table with 1,000 rows of data and you need a formula or a numbered list in the adjacent column. Instead of painstakingly dragging that tiny fill handle down your screen, just give it a quick double-click.
That's it. Excel intelligently fills the series all the way down, stopping precisely at the end of your data set. This one move can save you minutes of scrolling, especially with large spreadsheets. It’s a game-changer.
Unlocking More Options with a Right-Click
While the standard left-click-and-drag gets the job done for simple tasks, using your right mouse button is like opening a secret door to more powerful options. When you right-click and drag the fill handle, a special context menu pops up the moment you let go.
This menu gives you much finer control over how Excel fills your data. It’s packed with incredibly useful, specialized commands.
- Fill Weekdays: Perfect for project plans or work schedules. This option automatically populates a date series while skipping Saturdays and Sundays.
- Fill Months/Years: A must-have for financial reporting. You can instantly create timelines with monthly or yearly increments.
- Linear/Growth Trend: This is where it gets really interesting. You can forecast data by creating a series that follows a steady linear trend or even an exponential growth curve.
I use the right-click trick all the time for forecasting and financial modeling. It gives you instant access to complex series generation without having to mess around with formulas.
The CTRL Key Toggle and Other Quick Tricks
Another essential shortcut to have in your back pocket involves the CTRL key. Holding down CTRL while you drag the fill handle completely flips its default behavior.
For example, if Excel wants to create a series (like 1, 2, 3), holding CTRL will force it to just copy the original cell's value instead (1, 1, 1). If it's already copying, CTRL will make it create a series. This is super handy for quickly switching between copying and filling on the fly.
Think of these shortcuts like mental flashcards for Excel; the more you practice them, the more they become second nature. Speaking of which, if you're looking for other ways to boost your learning, our guide on how to use flashcards for studying has some great tips.
Getting these pro tips into your regular workflow will make your time in Excel much more efficient. The double-click saves you from endless scrolling, the right-click drag unlocks powerful fill options, and the CTRL key gives you instant control. Make these a habit, and you'll speed through your data tasks.
What to Do When Autofill Goes Wrong
Even a feature as reliable as Autofill can have its off days. When you’re deep in your workflow, an unexpected hiccup can really throw a wrench in things. But don't worry—most of the common problems are surprisingly easy to fix. Let's dig into what usually goes wrong and how to get things working again.
Why Is Autofill Just Copying My Cells?
This is probably the most common frustration I hear about. You type a 1, grab the fill handle, and drag down, hoping for a nice, clean sequence: 1, 2, 3, 4. Instead, you get a column of ones: 1, 1, 1, 1. Infuriating, right?
This happens because Excel is trying to guess your intention, and with only one number, it defaults to copying. You need to give it a stronger hint.
The fix is simple: give it a pattern.
- Type 1 in the first cell.
- Type 2 in the cell right below it.
- Now, select both cells and drag the fill handle.
By selecting two cells, you're explicitly telling Excel, "Hey, the pattern is to add one each time." It'll get the message and fill the series correctly.

My Autofill Stopped Halfway Down the Column!
Here’s another classic scenario. You’ve got a column with 500 rows of data, so you double-click the fill handle to populate the adjacent column… but it stops dead at row 250. What gives?
Nine times out of ten, this is caused by a blank cell in the guide column. The double-click shortcut uses the adjacent column to figure out where to stop. The moment it hits an empty cell, it assumes you've reached the end of your data.
To get around this, you can either fill in the blank cell that's causing the problem or just click and manually drag the fill handle all the way down to where you need it to go.
Is Flash Fill Broken? It’s Not Working.
Flash Fill is like Autofill's smarter, mind-reading cousin, but sometimes it just won't play along. You start typing out first names from a column of full names, expecting it to magically fill the rest, and… nothing.
There are a few culprits to check for:
- Is it even turned on? Flash Fill is usually on by default, but it can get switched off. Double-check your settings by going to
File > Options > Advancedand making sure "Automatically Flash Fill" is enabled. - Your data might be too messy. Flash Fill is smart, but it's not a miracle worker. It needs a clear, consistent pattern to latch onto. If your source column has random extra spaces, weird formatting, or missing bits of info, Flash Fill will get confused and give up.
- The columns aren't next to each other. For best results, the column you're typing in should be directly adjacent to the source column. If there's an empty column in between, Flash Fill might not make the connection.
Key takeaway: When Autofill or Flash Fill acts up, the problem is almost always in the source data. Before you do anything else, take a close look at your cells and check for inconsistencies, blank spaces, or anything that breaks the pattern.
A Word of Warning: The Dangers of Autofill in Data Analysis
For all its convenience, autofill in Excel should be used with extreme caution in serious data analysis or research. Using it to fill in missing data points—a process called imputation—can create misleading or just plain wrong results. It introduces patterns that weren't there to begin with, which can skew your entire analysis.
A now-famous incident from 2023 involved an economics paper on green innovations where researchers were accused of using Autofill to patch up gaps in their dataset. This led to a huge controversy and highlighted just how easily the tool can be misused, potentially compromising the integrity of the data. You can read more about the undisclosed tinkering in this economics paper to see how serious the consequences can be. Always think twice before using Autofill to generate data you don't actually have.
Your Questions About Excel Autofill Answered
As you start weaving Excel's Autofill into your daily workflow, you're bound to run into some quirky situations and "what if" moments. Let's tackle some of the most common questions that pop up, so you can handle the nuances of this powerful tool like a pro.
Can I Use Autofill on Filtered or Hidden Rows?
This is a big one, and a frequent source of frustration. When you filter a dataset and then drag the fill handle down, Excel doesn't just fill the visible cells—it plows right through your hidden rows, too. This can be a disaster, accidentally overwriting data you carefully filtered to protect.
So, how do you fill only the cells you can see? It requires a slightly different technique than just dragging the little black cross.
- First, type your value or formula into the top visible cell of your target range.
- Next, select the entire range you want to fill, including all the hidden cells in between.
- Now for the magic trick: press F5 to bring up the "Go To" dialog box. Click the "Special…" button and choose "Visible cells only."
- With just the visible cells selected, press Ctrl + D. This shortcut tells Excel to fill down, but it will only act on the cells you've specifically selected, leaving your hidden data untouched.
It's a few extra clicks, but this method is a lifesaver for keeping your filtered data clean.
Is It Possible to Disable Autofill Completely?
While Autofill is a huge time-saver, sometimes that little fill handle gets in the way. Maybe you just want to select cells or move them, and you keep accidentally triggering a fill. If it's driving you crazy, you can turn it off.
Just head over to File > Options > Advanced. In the "Editing options" area, you'll find a little checkbox labeled "Enable fill handle and cell drag-and-drop." Uncheck it, and the fill handle will disappear. Just don't forget to turn it back on when you're done!
Disabling the fill handle can be a good temporary solution for certain tasks, but it's a core Excel feature for a reason. Most experienced users find it's better to leave it on and just be mindful of where you're clicking and dragging.
How Does Autofill Work with Non-English Text?
Excel is smarter than you might think. Its built-in lists for days of the week and months of the year are language-aware. If your copy of Office is set to Spanish, typing "enero" and dragging the handle will produce "febrero," "marzo," and so on, just as you'd expect.
For any other text that isn't a default list, however, Autofill will simply copy the cell's contents. This is where creating your own custom lists really shines, especially when you're working with unique product names, specialized terms, or any other series in a different language.
Building custom lists puts you in complete control. Of course, remembering all these custom lists and Excel's countless functions can be a lot to juggle. It helps to use specific techniques for improving memory retention to make sure these powerful skills stick. Mastering these details is what separates a casual user from a true Excel power user.
Ready to conquer the AZ-204 exam? With AZ-204 Fast, you get access to interactive flashcards, dynamic practice exams, and detailed cheat sheets designed to get you certified in just a few weeks. Start your journey to becoming a certified Azure Developer by checking out our tools at https://az204fast.com.
Leave a Reply