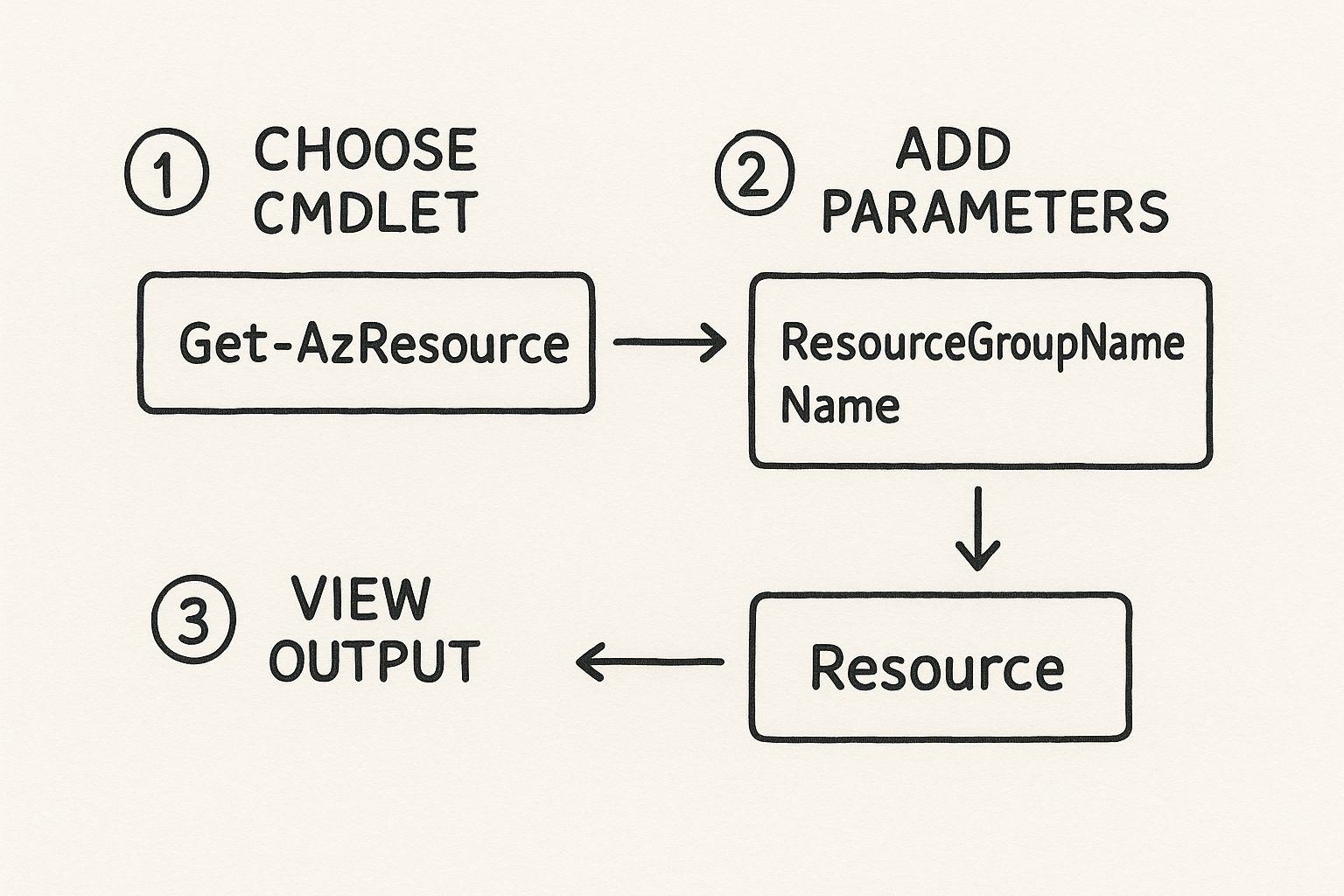
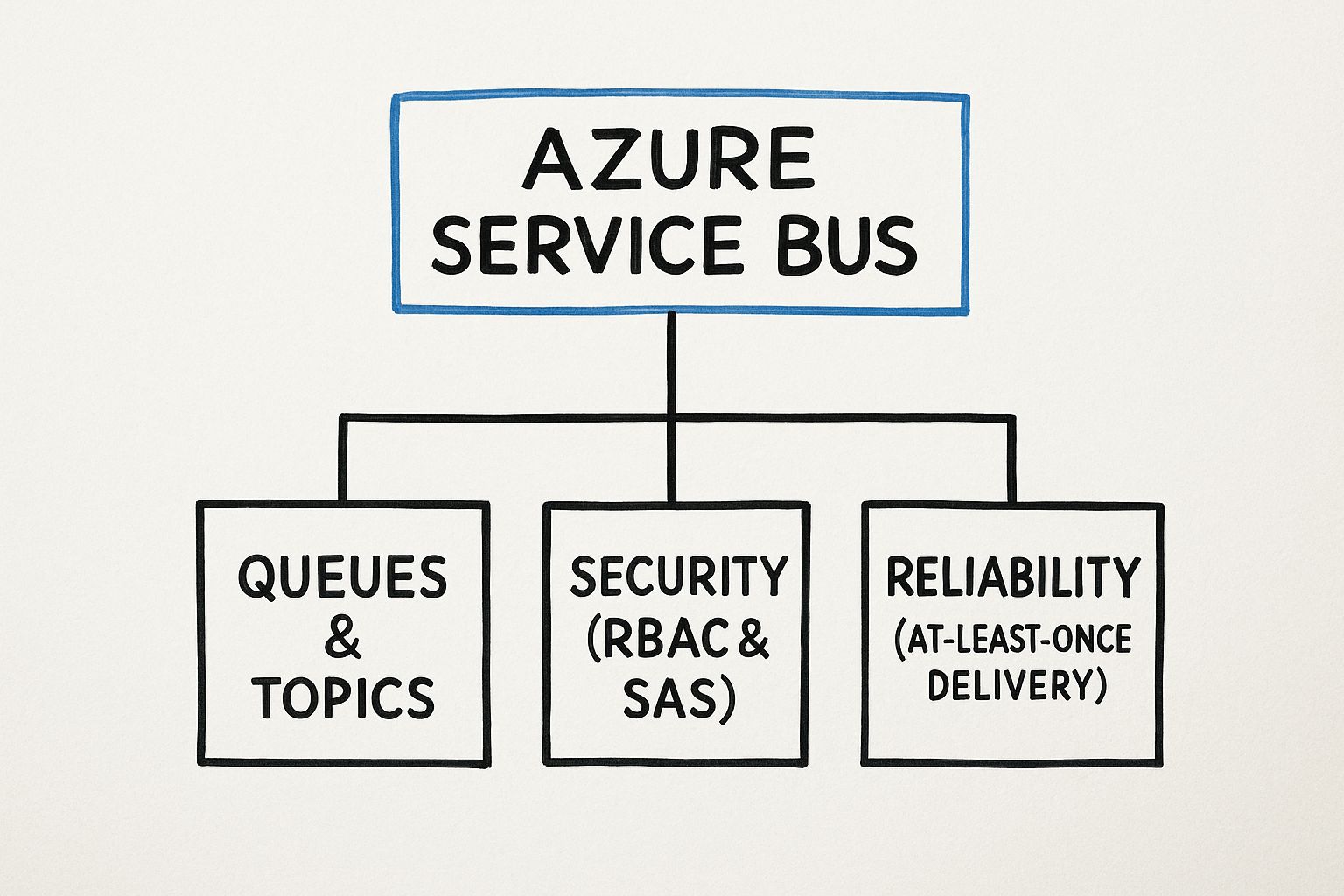
So, you need to open up your SQL Server to the outside world. This isn't just a simple switch you flip; it’s a deliberate process involving a few key steps. You'll need to enable the right network protocol, tell SQL Server to actually listen for incoming connections, and then poke a hole in your firewall to let the traffic through. Getting these steps right is what makes your database available to the applications and people who need it.
Why Bother with Remote SQL Server Access?
Before we jump into the "how," let's quickly cover the "why." In almost any real-world setup, your database can't live in a silo. Making it accessible from other machines isn't just a nice-to-have; it’s the backbone of modern application design. Your database needs to talk to other parts of your system, and enabling remote access is how you make that conversation happen.
Think about a standard web application. You almost never have your web server and database server on the same machine. For performance, security, and scalability, they're kept separate. That web server needs to reach across the network to query the SQL Server to do its job. It's the same story with business intelligence tools like Power BI or Tableau. Your data analysts are running these on their own computers, and they need a direct line to the database to build their reports and dashboards.
Here are a few classic scenarios I see all the time where remote access is a must:
- Websites and Apps: The front-end and back-end logic run on different servers, all communicating with a central SQL Server.
- Remote Database Management: As a DBA, you need to manage servers from your own workstation. You can't be expected to log into the server console for every little task.
- Connecting Services: Your SQL Server often needs to sync data with other systems, like a data warehouse or a cloud service.
This push for connected data is a huge deal. The market for what's called SQL Server Transformation—which includes making data more accessible—was valued at roughly USD 20.7 billion in 2025 and is expected to hit USD 54.2 billion by 2035. That explosive growth shows just how essential it is to get this right. If you're interested in the market trends, you can dig deeper into this detailed report on SQL Server transformation.
But let’s be clear: opening your SQL Server to remote connections also opens it up to potential threats. Every step we take from here on out will be viewed through a security lens. Connectivity is the goal, but security is the priority.
Switching On TCP/IP in SQL Server Configuration
First things first: your SQL Server won't talk to the outside world until you tell it to. For security, most fresh SQL Server installations come with network connectivity turned off by default. So, your initial task is to dive into the SQL Server Configuration Manager and flip the right switch.
This utility is your control panel for all things related to SQL Server services and network protocols. It's a bit hidden away—you won't find it in the Start Menu alongside your other SQL tools. The quickest way to pull it up is by searching for SQLServerManager<version>.msc. For instance, if you're running SQL Server 2019, you’d search for SQLServerManager15.msc.
Once you've got it open, you'll see a slightly old-school interface, but don't let that fool you; its purpose is direct and powerful. Your target is the SQL Server Network Configuration node in the pane on the left.
Finding Your Way Through the Configuration Manager
When you expand the network configuration node, you'll see a list of protocols for every SQL Server instance on that machine. You need to zero in on the specific instance you want to open up for remote access. This is usually MSSQLSERVER for a default instance, but it could also be a custom name if you're working with a named instance.
After selecting your instance, look to the right-hand pane. You'll find a few protocols listed, like Shared Memory and Named Pipes. Your focus, however, is solely on TCP/IP.
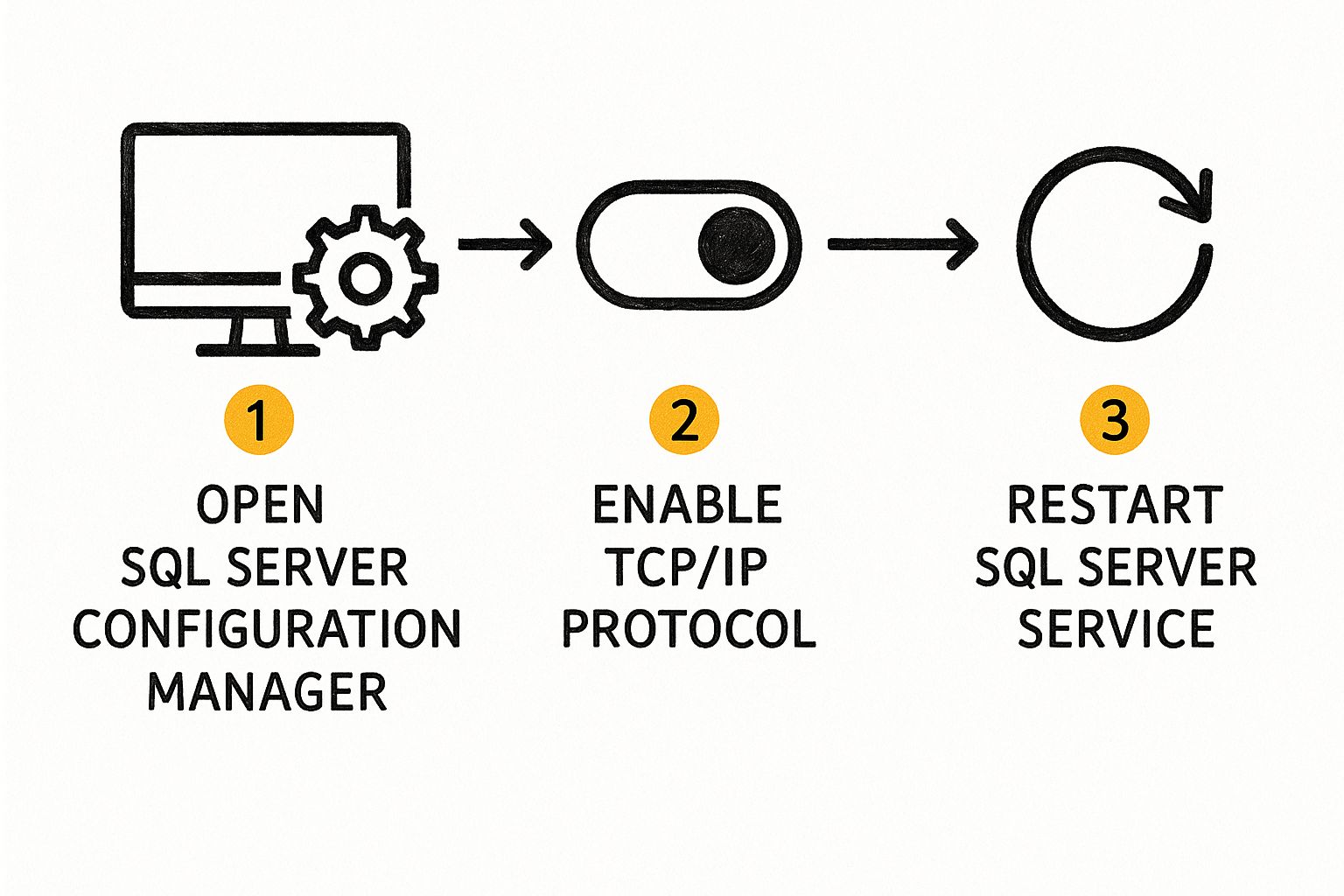
Right-click on TCP/IP and choose Enable. You'll immediately get a small pop-up warning that the change won't take effect until the service is restarted. This is a critical step that trips a lot of people up. Just enabling the protocol doesn't complete the job—you have to restart the SQL Server service itself for it to begin listening.
My Two Cents: Think of this as the master switch. If TCP/IP is disabled, nothing else you do with firewall rules or server settings will matter. The server simply won't be listening for network requests.
Making the Changes Stick
With TCP/IP enabled, it's time to make it official by restarting the SQL Server service. The good news is you can do this right from the Configuration Manager.
- Head over to the SQL Server Services node in the left-hand pane.
- Locate the SQL Server service that corresponds to your instance, like
SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER). - Just right-click the service and select Restart.
The service will quickly stop and start back up. Once it's running again, it's now actively listening for connections using the TCP/IP protocol. You've just knocked out the first major hurdle. The next logical step is getting your firewall to let that traffic through.
Configuring Your Server for Secure Connections
Just because TCP/IP is active doesn't mean your SQL Server is ready for company. Think of it this way: you've turned on the lights, but the front door is still locked. The next step is to explicitly tell your SQL Server instance that it's okay to accept connections from other machines.
This critical permission is managed right inside SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). Go ahead and open SSMS and connect to your instance. In the Object Explorer panel, find the very top node—your server's name—right-click it, and choose Properties. This opens the command center for your entire instance. From here, click on the Connections page in the left-hand pane.
Look for the checkbox that says Allow remote connections to this server. This is the master switch. You need to make sure it's checked. Without this, all your other configuration work is for nothing; the server will simply refuse any connection that isn't coming from the local machine.
The Critical Authentication Decision
Now for arguably the most important decision you'll make in this process: how will users prove who they are? In the same Server Properties window, click over to the Security page. This is where you set the authentication mode.
Your choice here has significant security implications, so it’s important to understand the difference.
SQL Server Authentication Modes Compared
| Feature | Windows Authentication Mode | Mixed Mode (SQL Server and Windows Authentication) |
|---|---|---|
| Who It's For | Environments where all users and applications are on the same Windows domain. | Environments with non-domain users, legacy applications, or specific third-party tools that require SQL logins. |
| Security | More secure. Leverages Active Directory's robust policies (password complexity, expiration, account lockouts). No passwords sent over the network. | Less secure by nature. You are now responsible for managing SQL login passwords. Requires diligent password policies. |
| Management | Centralized in Active Directory. DBAs don't manage individual passwords. | Requires manual management of SQL logins and passwords directly within SQL Server. |
| Best Practice | The default and recommended setting for most corporate environments. | Use only when absolutely necessary. If you enable it, you must secure the 'sa' account with a very strong password and disable it if possible. |
In my experience, you should always stick with Windows Authentication unless you have a compelling, undeniable reason not to. It's simply more secure and easier to manage.
If you find yourself needing Mixed Mode—perhaps for a specific web application or a partner connecting from outside your network—you’re also taking on a serious responsibility.
Enabling Mixed Mode isn't just a setting; it's a security commitment. You must enforce a strong password policy for all SQL logins, including complexity, history, and expiration. A weak 'sa' password is one of the most common and dangerous security vulnerabilities I see in the wild.
Navigating Different SQL Server Versions
The version of SQL Server you're running also plays a part. The landscape is dominated by a few key players; recent data shows SQL Server 2019 still holds a 44% share, but the newer SQL Server 2022 has quickly grown to 21%.
Why does this matter? Newer versions come with more robust and streamlined security features for remote access, like improved encryption. Sticking with a supported, modern version isn't just about new features—it's a critical security practice.
For organizations running a hybrid setup, the lines between on-premises and cloud are blurring. It's now quite common to sync local user accounts with the cloud. If this sounds like your environment, you might want to look into how to handle https://az204fast.com/blog/azure-active-directory-sync. This approach centralizes your identity management, which can dramatically strengthen your security posture for all connections, remote or otherwise.
Navigating Windows Firewall for SQL Server
So, you’ve sorted out the protocols and your server settings are dialed in. Now for the final boss: the Windows Defender Firewall. In my experience, if you can't get a remote connection to SQL Server, a misconfigured firewall is the culprit 9 times out of 10. It’s that silent gatekeeper that just denies traffic, leaving you staring at a "cannot connect" error and scratching your head.
Let's cut through the confusion. The goal is to create a specific inbound rule that tells the firewall to let traffic through to your SQL Server instance. You'll do this from inside the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security tool.
Creating Program-Based Firewall Rules
The most foolproof way to do this is by creating a rule that points directly at the SQL Server program file, which is sqlservr.exe. I strongly recommend this method over a port-based rule, especially if your SQL Server is using dynamic ports. Why? Because dynamic ports can change every time the service restarts, and a program-based rule doesn't care—it just works.
Here’s the game plan for the Database Engine rule:
- Inside the firewall tool, find Inbound Rules on the left, right-click it, and hit New Rule.
- When the wizard pops up, select the Program rule type.
- You'll be asked for the program path. Browse to where
sqlservr.exelives. It’s usually buried in a path similar toC:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL<version>.<InstanceName>\MSSQL\Binn\. - Next, choose Allow the connection.
- Apply the rule to the network profiles that make sense for your environment (Domain, Private, Public). Finish by giving it a clear name, something like "SQL Server – DB Engine Access," so you know what it is later.
This approach essentially gives the sqlservr.exe application a free pass through the firewall, no matter what port it decides to listen on.
Pro Tip: Don't forget about the SQL Server Browser service! If you're using a named instance or relying on dynamic ports, this service is non-negotiable. You'll need to create a second inbound rule for it, this time pointing to the
sqlbrowser.exefile. You can typically find it inC:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SQL Server\90\Shared\.
Why a Static Port Is Often Better
While program-based rules are great for dynamic environments, many seasoned DBAs prefer a more predictable setup. By configuring your SQL Server instance to use a static port (like the classic default of 1433), you create a more secure and straightforward environment. It just makes firewall management simpler because you know exactly which door needs to be unlocked.
If you go the static port route, you can create a port-based firewall rule instead. Some argue this is slightly more performant and it’s definitely considered a standard security practice in many corporate environments. You're trading a little extra configuration work upfront for a whole lot of long-term stability.
As security becomes a bigger and bigger deal, these kinds of specific firewall rules are essential. Modern best practices often mean locking down everything and only opening what’s absolutely necessary, usually in combination with VPNs and full encryption. This security-first approach is a major driver behind the adoption of newer versions like SQL Server 2022, which offers enhanced security features. You can see how these trends are playing out across the industry in this insightful SQL Server security practices report.
For organizations blending on-premise systems with the cloud, identity management is another key piece of the security puzzle. Looking into solutions for Azure Active Directory integration can centralize how users are authenticated, adding another powerful layer of protection for your remote connections.
Solving Common SQL Connection Problems
Even after following every step perfectly, you might still run into the dreaded error message: "A network-related or instance-specific error occurred while establishing a connection to SQL Server." This is one of the most infamous and frustrating errors for anyone working with SQL Server. It tells you something is wrong but gives you almost no clue what it is.
When you see this, take a breath. The key is to troubleshoot systematically, not to start changing settings at random. Think like a detective and work your way from the client machine back to the server to isolate where the connection is failing. Is the server even reachable? Is the SQL instance itself the problem? Or is it a simple authentication mix-up?
Your Diagnostic Toolkit
One of the most powerful yet simple tools in your arsenal is a Universal Data Link (UDL) file. It's a lifesaver. On the client machine trying to connect, just right-click your desktop, create a new text document, and rename it to something like test.udl.
Double-clicking that file opens the Data Link Properties window—a generic connection utility that’s incredibly useful for diagnostics.
Here, you can plug in your server name and credentials and test the connection directly. The feedback it provides is often far more specific than what your application will give you. For instance, if the connection hangs for 30-60 seconds before failing, you're almost certainly looking at a network or firewall problem. If it fails instantly with an "invalid login" message, you know you've reached the server, and the issue is with the username or password.
Another fantastic tool is the command-line utility SQLCMD. From a command prompt on the client, you can try connecting directly, completely bypassing your application's code. For a named instance, the command looks like this:
SQLCMD -S YourServerName\YourInstanceName -U YourSqlLogin -P YourPassword
This gives you a raw, unfiltered test of connectivity.
Remember, troubleshooting is all about isolation. Using a UDL file or
SQLCMDfrom the client machine helps you figure out if the problem is with the network and firewall or something in your application's connection string. This one step can save you hours of frustrated guesswork.
The Troubleshooting Checklist
When you're trying to allow remote connections to SQL Server and keep hitting a wall, run through this quick checklist:
- Is the SQL Browser Service Running? This is a classic culprit for named instances. If this service is stopped, clients have no way of finding out which port your instance is listening on.
- Can the Client Reach the Server? Try a simple
pingcommand with the server's name. Ifpingfails, you're dealing with a DNS problem or a more fundamental network block that has nothing to do with SQL Server itself. - Is the Firewall Rule Correct? Go back and double-check the inbound rule on the server. Make sure it's enabled and correctly configured for either the SQL Server program (
sqlservr.exe) or the specific TCP port. A typo here is all it takes to block everything.
In larger environments, automating these checks can be a real game-changer. If you manage SQL Server on Azure VMs, scripting these diagnostics can save a ton of time. For a deeper dive into automation, you might find our guide on the Azure PowerShell module helpful.
By methodically working through these common failure points, you can turn that vague, frustrating error into a clear, solvable problem.
Frequently Asked Questions About Remote SQL Access
https://www.youtube.com/embed/lJ_WRSN_wD0
Even when you follow a guide perfectly, setting up remote SQL Server access always seems to have a few lingering questions. Let's walk through some of the common ones I hear all the time to clear up any confusion and make sure your setup is both functional and secure.
Should I Use the Default Port 1433 or a Custom Port?
While using the default port 1433 is easy, it’s like putting a giant "SQL Server here!" sign on your network. It’s the very first place automated bots and attackers will look. My advice? For any production server, especially one with sensitive data, switch to a custom, non-standard port.
This is a classic example of "security through obscurity." It won't single-handedly stop a dedicated attacker, but it's an incredibly simple and effective way to sidestep the vast majority of low-effort, automated scans looking for easy prey on the default port.
Is a VPN Required to Connect to SQL Server Remotely?
Technically, no, the connection will work without one. But from a security standpoint, it’s non-negotiable. Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) is an absolute must for secure remote access. The VPN wraps all the traffic between you and the server in an encrypted tunnel, shielding your data from prying eyes.
Think of it this way: exposing SQL Server directly to the internet is a massive risk. A VPN creates a secure, private corridor that dramatically shrinks your attack surface. It's the industry-standard method for secure remote database administration for a reason.
The need for secure remote access isn't going away; it's accelerating. You just have to look at the latest SQL Server population trends to see how many environments, including cloud services like Azure SQL, are built for remote connectivity.
Can I Allow Connections From Only Specific IP Addresses?
Absolutely, and you definitely should. This is one of the most effective security layers you can add. Instead of creating a firewall rule that allows traffic from "Any IP address," lock it down.
Here’s how you do it:
- Open your firewall rule in Windows Defender Firewall.
- Go to the Scope tab.
- Under the "Remote IP addresses" section, choose "These IP addresses."
- From there, you can add a list of the specific, static IP addresses of the machines that need to connect.
This is a powerful gatekeeping measure. It ensures that only pre-approved clients can even knock on the door, blocking all other traffic at the network's edge.
How Do I Find My SQL Server Instance Name?
It happens to the best of us, especially when you're juggling multiple servers. The quickest and most reliable way to find your instance name is to log into the server locally using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Once you're connected, just run this simple T-SQL query:
SELECT @@SERVERNAME
The query will return the full name you need, typically in the format of YourServerName\YourInstanceName. If you're using a default instance, it will just show the server's name. You'll need this exact string when setting up your connection from a remote machine.
Preparing for your Azure Developer exam? Stop cramming and start learning effectively. AZ-204 Fast offers a smarter way to study with interactive flashcards, adaptive practice exams, and progress analytics designed to get you AZ-204 certified, faster. See how our system works at https://az204fast.com.